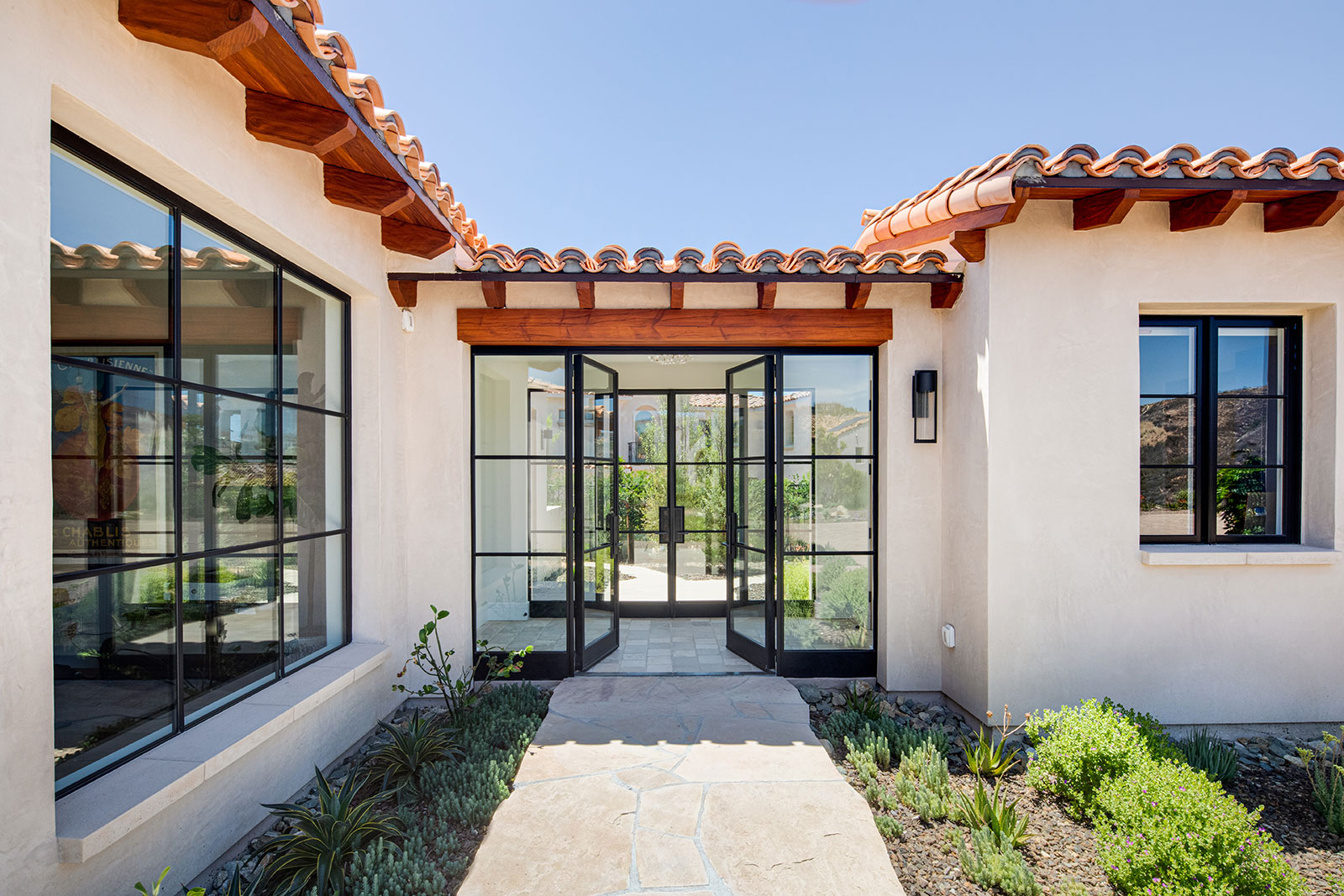
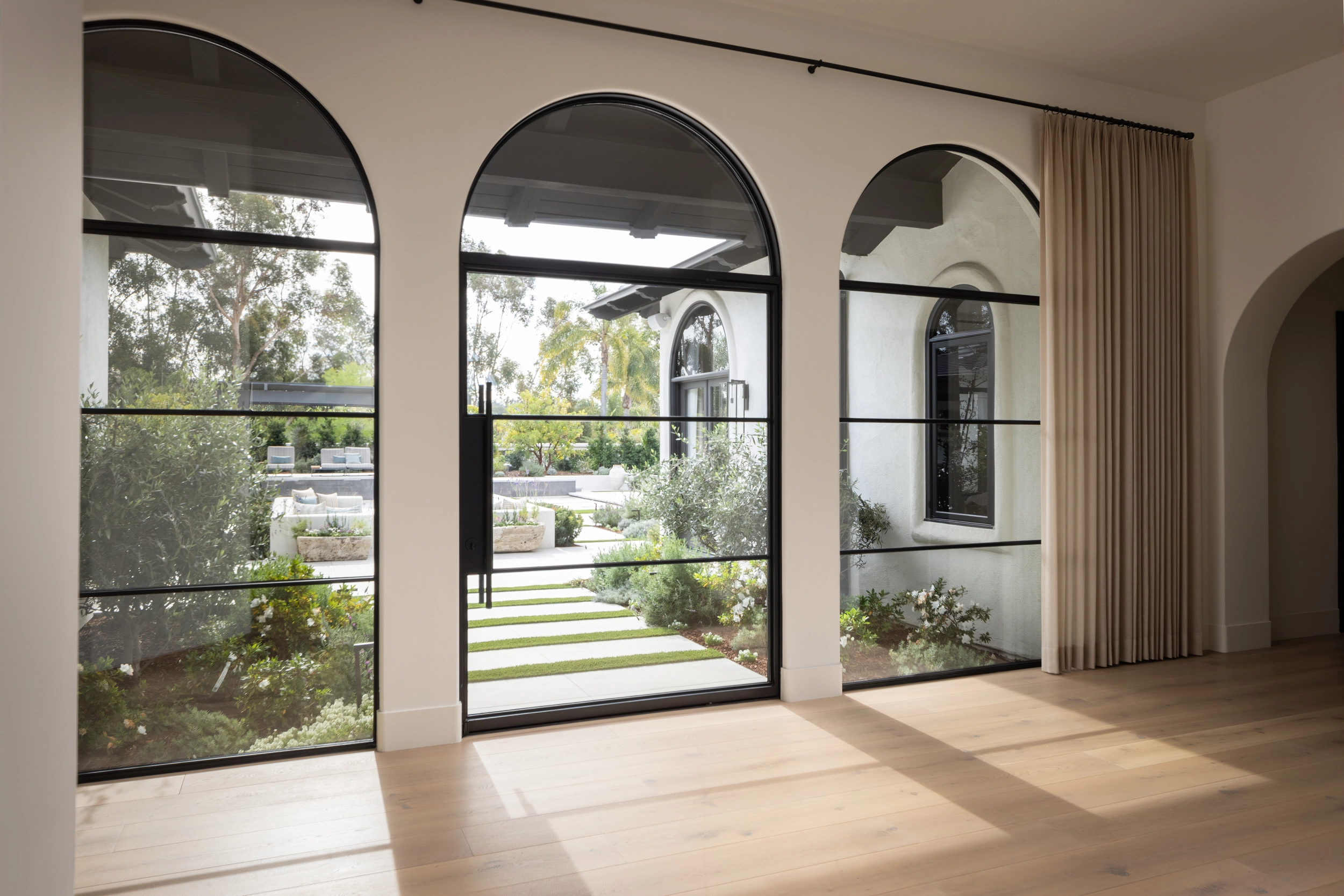
- PRODUCTS
OUR PRODUCTS
- WINDOWS
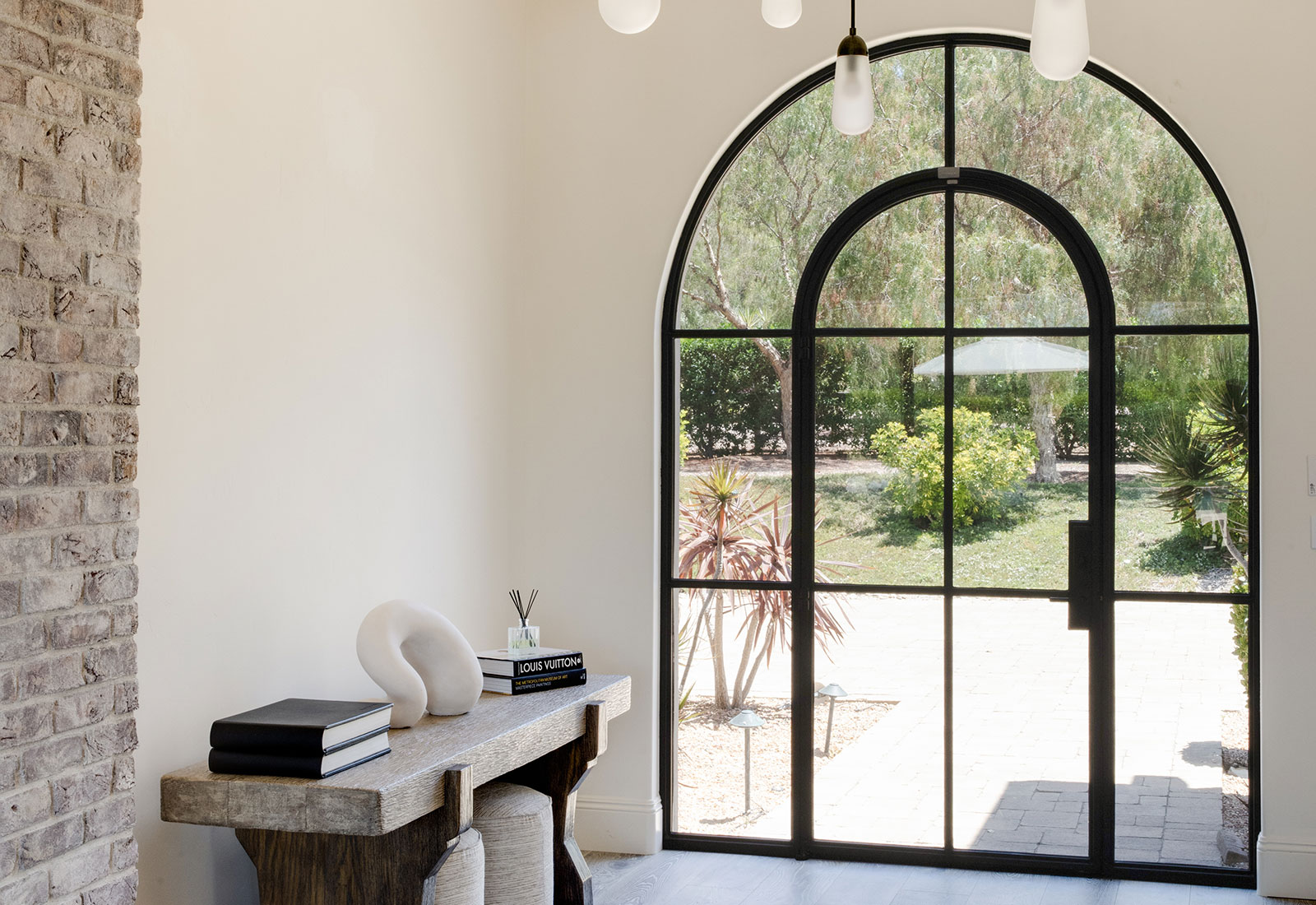
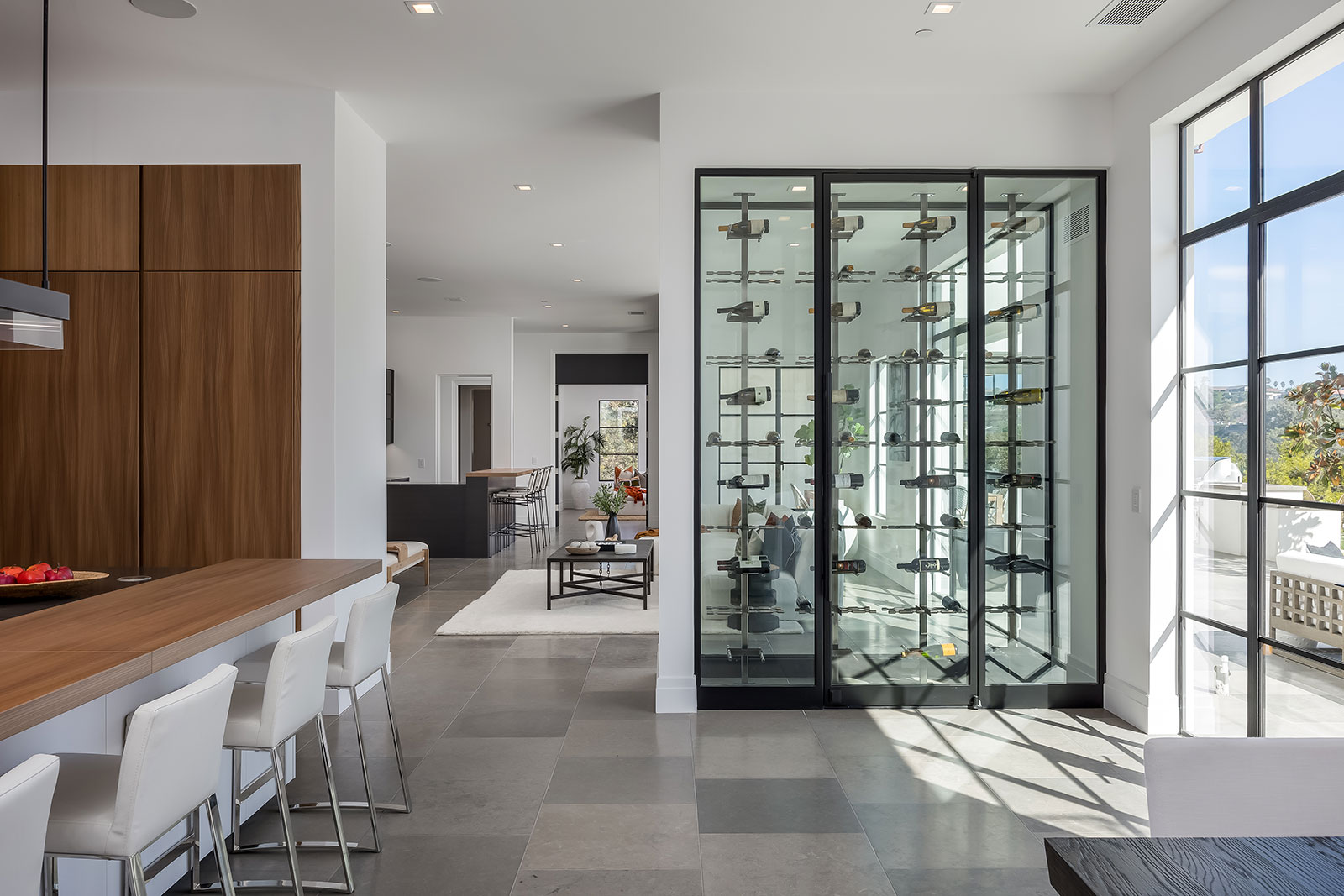
Fixed Window
Casement Window
Awning Window
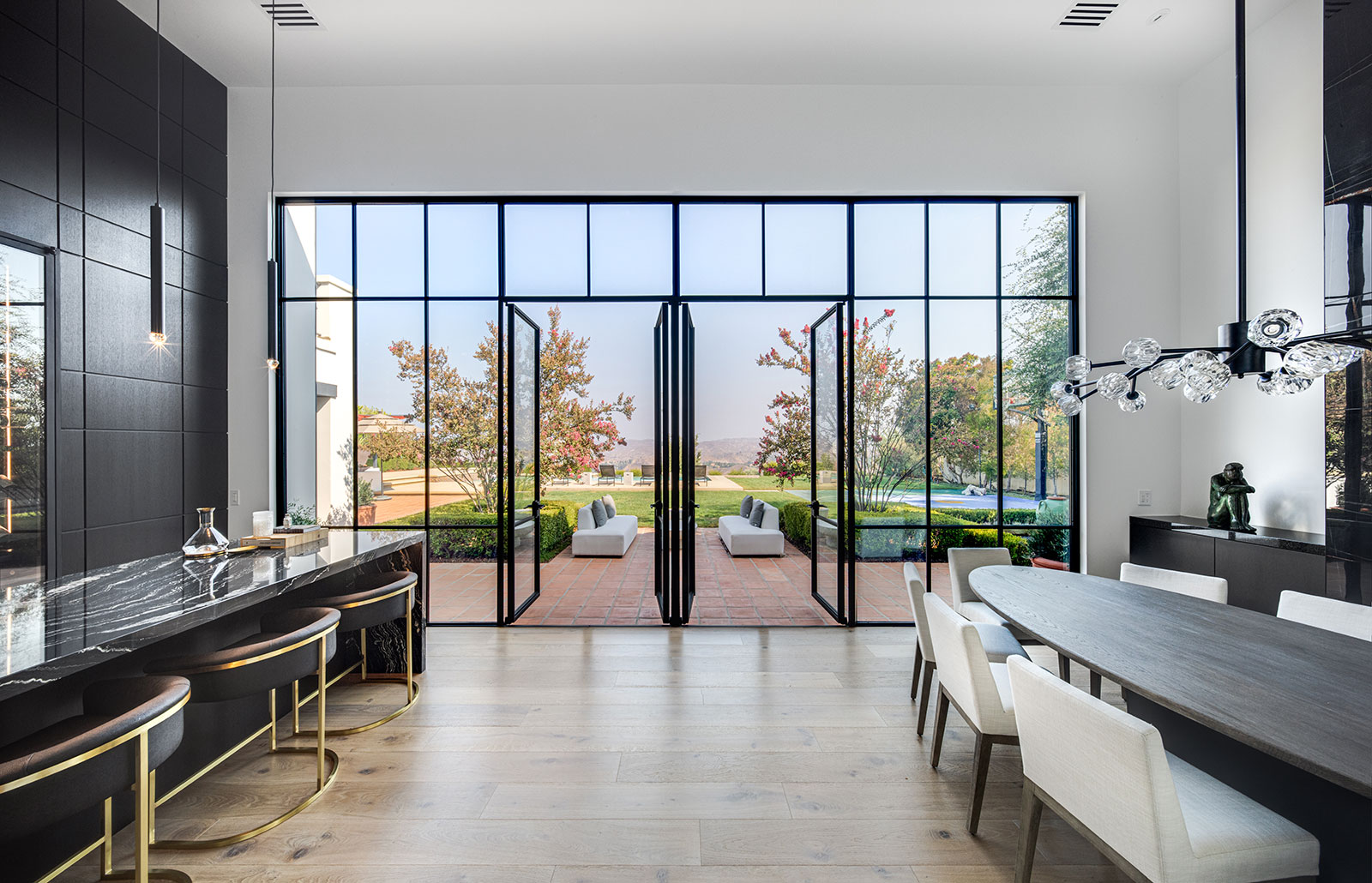
Bi-Fold Window
Sliding Window
Pivot Window
- SWING
Single Swing
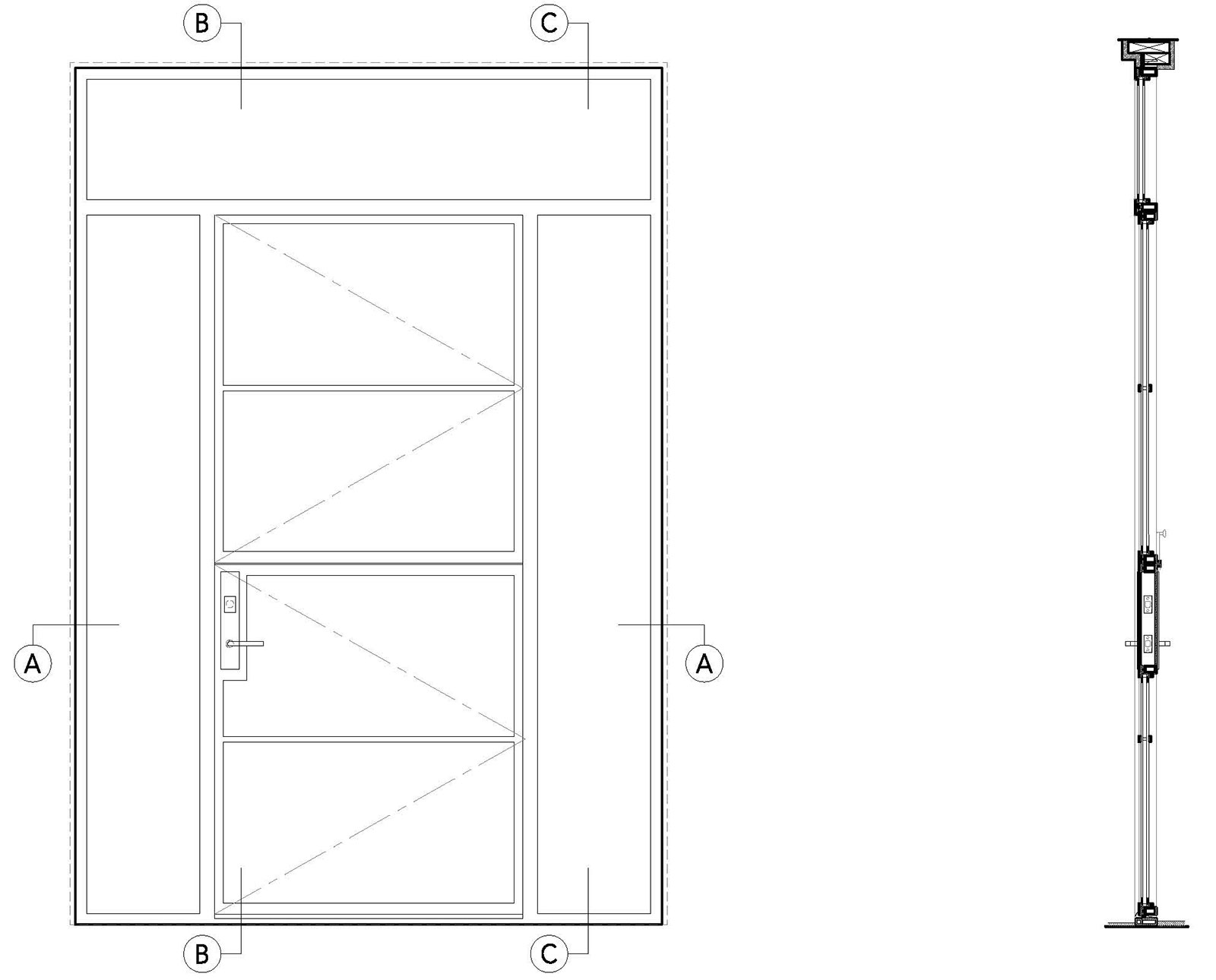
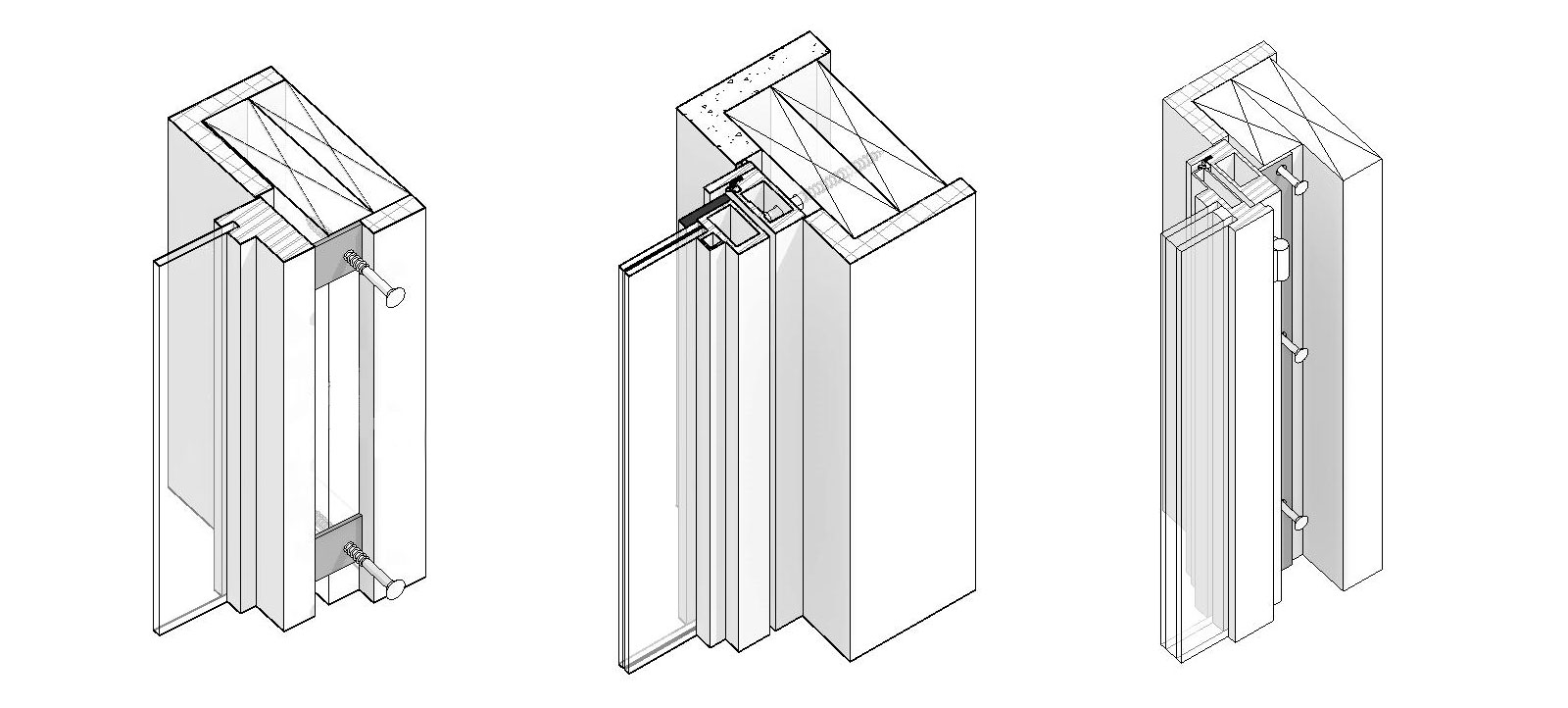
Dutch Door
French Door
- SLIDING
Multi-Slider
Pocket Multi-Slider
Lift And Slide
- BIFOLD
Outswing Fold
Center Fold
Inswing Fold
- PIVOT
Pivot Door
Pivot Window
- SERIES
- ABOUT
- FINISHES
- PROFESSIONALS
- FIND A DEALER
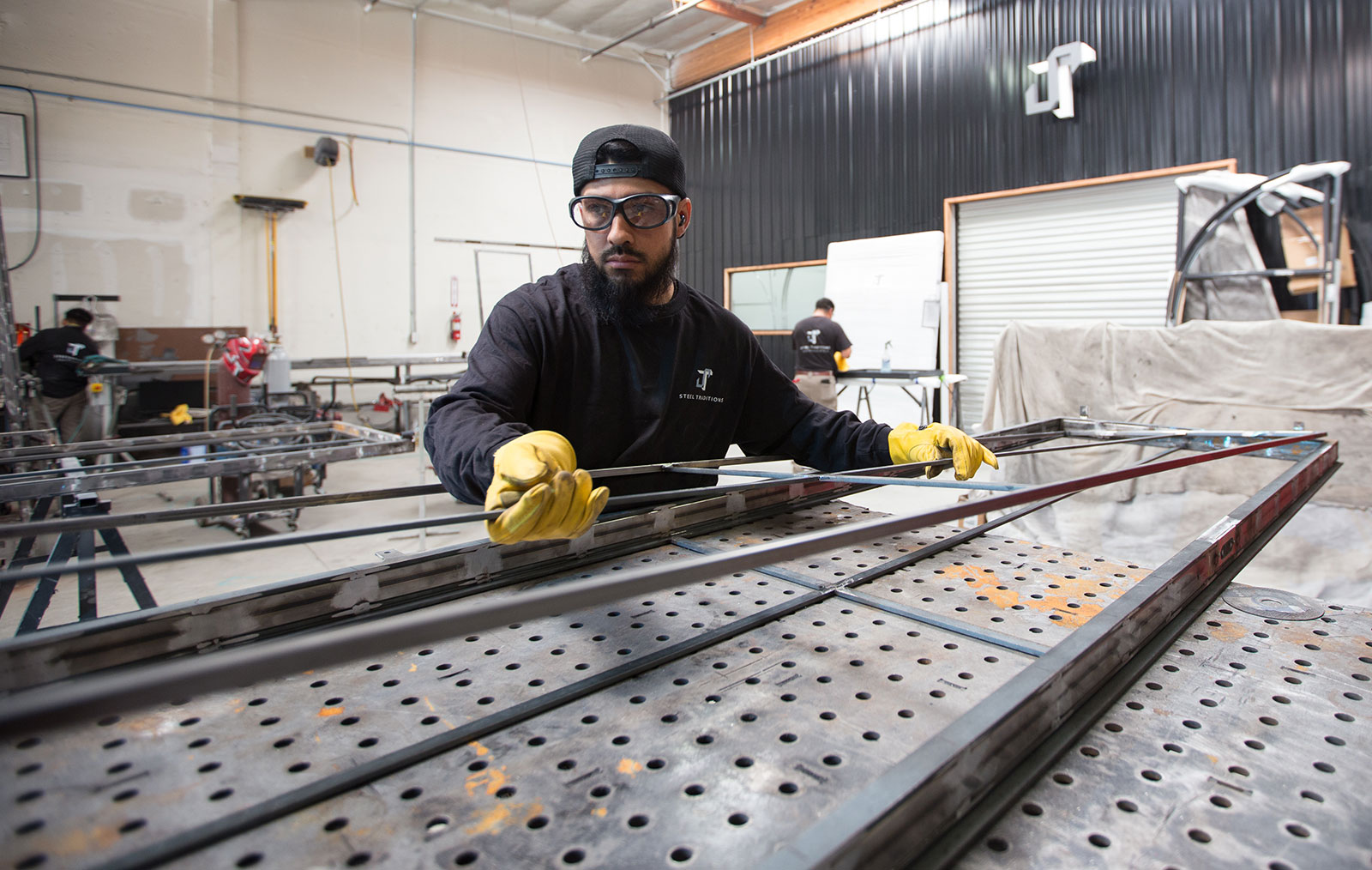
OUR HEADQUATERS & MANUFACTURING FACILITY IN VISTA CALIFORNIA
CONTACT US
OUR HEADQUATERS & MANUFACTURING FACILITY IN VISTA CALIFORNIA
OUR HEADQUATERS & MANUFACTURING FACILITY IN VISTA CALIFORNIA
- PRODUCTS
OUR PRODUCTS
- WINDOWS
Fixed Window
Casement Window
Awning Window
Bi-Fold Window
Sliding Window
Pivot Window
- SWING
Single Swing
Dutch Door
French Door
- SLIDING
Multi-Slider
Pocket Multi-Slider
Lift And Slide
- BIFOLD
Outswing Fold
Center Fold
Inswing Fold
- PIVOT
Pivot Door
Pivot Window
- SERIES
- ABOUT
- FINISHES
- PROFESSIONALS
- FIND A DEALER
OUR HEADQUATERS & MANUFACTURING FACILITY IN VISTA CALIFORNIA
CONTACT US
OUR HEADQUATERS & MANUFACTURING FACILITY IN VISTA CALIFORNIA
OUR HEADQUATERS & MANUFACTURING FACILITY IN VISTA CALIFORNIA
- PRODUCTS
OUR PRODUCTS
- WINDOWS
Fixed Window
Casement Window
Awning Window
Bi-Fold Window
Sliding Window
Pivot Window
- SWING
Single Swing
Dutch Door
French Door
- SLIDING
Multi-Slider
Pocket Multi-Slider
Lift And Slide
- BIFOLD
Outswing Fold
Center Fold
Inswing Fold
- PIVOT
Pivot Door
Pivot Window
- SERIES
- ABOUT
- FINISHES
- PROFESSIONALS
- FIND A DEALER
OUR HEADQUATERS & MANUFACTURING FACILITY IN VISTA CALIFORNIA
CONTACT US
OUR HEADQUATERS & MANUFACTURING FACILITY IN VISTA CALIFORNIA
OUR HEADQUATERS & MANUFACTURING FACILITY IN VISTA CALIFORNIA